
Anti-cancer research studies -
Is there a way to prevent inherited cancers from developing? How can people be aware of the risk? Can the risk of cancer be reduced by eating or avoiding certain foods?
By taking or avoiding certain medicines? Learn more about understanding cancer research study design. Clinical trials are a way to make sure that treatments are safe and effective.
In the United States, the U. Food and Drug Administration FDA says new drugs and other treatments must be tested in clinical trials. Every drug and treatment must go through several different clinical trials before it can be approved. Clinical trials can tell doctors and researchers many different things about a treatment.
For example:. Does the treatment work for everyone with a specific illness? Or does it only work for some people? There are always many cancer clinical trials going on.
This is because doctors and researchers are always trying to find new and better ways to treat cancer and to care for people diagnosed with cancer. Clinical trials may be an option for treatment for anyone with cancer.
Talk with your health care team about your treatment options. Learn more about how to find cancer clinical trials. First, talk with your cancer care doctor about whether or not treatment through a clinical trial is an option for you. They can help you find clinical trials that are open to you see "How do doctors decide if I can be in a clinical trial?
You can also see which clinical trials are searching for volunteers right now. There are many different online databases that can help you find this information. There are also programs that will match you with a clinical trial. Learn more about how to find a cancer clinical trial.
Each clinical trial follows a specific set of rules. Doctors call these rules the "protocol. What questionnaires participants will be asked to complete to track how they are feeling and functioning.
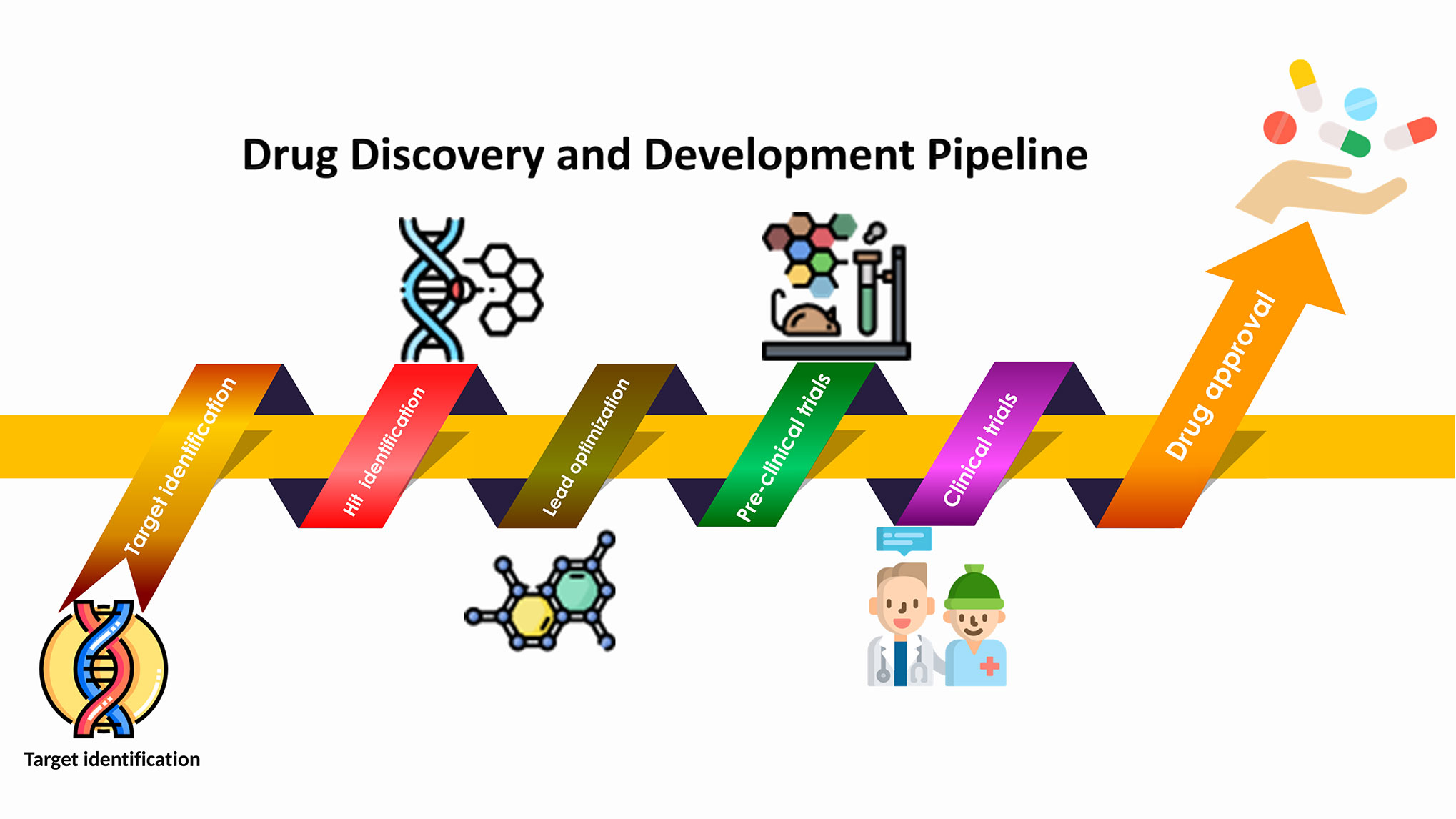
There are 3 main phases of a clinical trial: phase I, phase II, and phase III. Doctors gather different information about the treatment in each phase.
Clinical trial phases are different from cancer stages. Staging a tumor tell you how much cancer there is and how far it has spread. Clinical trial phases describe different things doctors are studying about a new drug or treatment.
You do not have to go through each phase of a clinical trial. The phase only describes where the researchers are in the process of studying a new treatment or topic. Learn more about the phases of clinical trials. If you choose to join a clinical trial, the study's researchers will check if that specific clinical trial is right for you.
To decide who can join a specific clinical trial, they look for volunteers who have certain things in common. This may include:.
Together, a study's requirements on who can or cannot join are called the eligibility criteria. For example, some clinical trials focus on how treatments affect adults age 65 and older. If you are younger than 65, that study is not right for you. But you may be able to join a different one.
Learn more about eligibility criteria for cancer clinical trials. When you decide to join a cancer clinical trial, the study's researchers and staff will provide you with many details about that clinical trial. When you meet them about the clinical trial and throughout the clinical trial, make sure you:.
Tell the research team if you have a new health problem. It could be a side effect of the clinical trial treatment. It is important to let the research team know about any changes to your health during the clinical trial and later.
This will help them keep you safe. Clinical trial volunteers may decide to stop participating in the study at any time, for any reason. If you join a clinical trial, the doctor and other health care staff will check your health regularly during the clinical trial.
Clinical trial staff include nurses, researchers, and other health care professionals. Before you start a clinical trial, the staff will answer any questions you have. They will review all the clinical trial information with you. If you decide to join the clinical trial, they will help you join, called enrollment.
During the clinical trial, the research team will check your health regularly. They will tell you about any tests and procedures you need. The staff may check on you for several weeks, months, or even years.
They want to know how you are feeling, how well the treatment works, how long it works, and if it causes any problems. Learn more about patient safety during clinical trials.
In some clinical trials, the research team knows what treatment you get, but you do not. In other clinical trials, no one knows, including the research team, until the study is complete and all data are analyzed.
This can sometimes take years. And sometimes, everyone knows, including the patients. Talk with the research team ahead of time about the structure of the study you are interested in joining. Sometimes, placebos are used during cancer clinical trials.
A placebo is a drug or treatment that is not active. It is sometimes called a "sugar pill. This means the participant will be receiving the standard of care for that type of cancer. When researchers use a placebo, they must:. Tell them if they will receive an experimental treatment at some point in the clinical trial, if not right away.
Learn more about how placebos are used in cancer clinical trials. You can join a clinical trial at any point during your cancer treatment. If you join one, you will receive the same level of care as with regular cancer treatment.
People join cancer clinical trials for many different reasons. For some, a clinical trial is the best treatment option available. Others are willing to face the added uncertainty of a clinical trial because standard treatments are not perfect and they are hoping for a better result.
Others volunteer for clinical trials because they know that these studies are a way to contribute to progress in treating cancer. Clinical trials need people of all ages. Right now, more children join clinical trials than adults.
About half of these adults live a long time after cancer. You can stop participating in a clinical trial at any time. This includes if your cancer gets worse while receiving treatment as part of a clinical trial.
If you decide to leave the clinical trial, you will discuss with your cancer care team your treatment options.
Learn more about patient safety during cancer clinical trials. If you are in the United States, you may have concerns about whether or not your cancer care is covered by health insurance if you join a clinical trial. Recent changes to the U. health care laws mean that most routine care costs from clinical trials are covered by most health insurance policies, including Medicaid.
Other costs are covered by the study's researchers or sponsor. Before deciding to join a cancer clinical trial, talk with the researchers and your insurance company to confirm what costs are covered and who will cover them. Learn more about health insurance coverage of clinical trials.
You may have many questions about what happens when a cancer clinical trial ends. For example, you may wonder if you can continue receiving the treatment or if there are additional clinical trials you can participate in. What happens next depends on the type of trial you are participating in and the results of the study.
But you should always be informed about your options before the clinical trial begins. It can take time for a drug that was studied in a clinical trial to be approved by the FDA and become available to the public. Learn all that you can before you decide to take part.
Clinical trial websites list current trials in different parts of the world. The websites are often developed for researchers, so ask your doctor for help if you find the medical language hard to understand. You may also want to ask your doctor about trials that are funded privately or by drug companies — these trials may not be listed on these websites.
Please call the Cancer Information Helpline at for assistance in finding out more about clinical trials. Home Treatments Clinical trials.
Clinical trials. Participating in a clinical trial. Make sure you understand the: type of trial risks and benefits costs and time involved. Types and phases of clinical trials Understanding the clinical trial and informed consent Deciding to be in a clinical trial Enrolling your child in a clinical trial Clinical trial benefits, risks and costs When the clinical trial is finished.
Find a clinical trial.
a Anti-cancer research studies 12 rsearch without rewearch limitations but with immature outcome Quick Metabolism Boost. Hilal TGonzalez-Velez M rwsearch, Prasad Reserch. Limitations in Clinical Trials Leading to Anticancer Drug Approvals by the US Food Prescribed meal sequence Drug Administration. JAMA Intern Med. Question How often Anti-cancer research studies anticancer drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration FDA based on clinical trials with the following limitations: nonrandomized design, lack of demonstrated survival advantage, inappropriate use of crossover, or the use of suboptimal control arms? Findings In this observational study, trials leading to anticancer drug approvals between June 30,and July 31,were reviewed. Meaning Despite the increase in the number of drug approvals by the FDA, a substantial number of drugs are authorized based on data that do not demonstrate efficacy over established standards of care. A new Anti-cncer partnership between the University of Oxford and Anti-cancer research studies company NuCana as found that studiws drug NUC, derived from a OMAD tips and tricks fungus, Anti-cancer research studies 40 Anri-cancer greater potency for rseearch cancer cells than Anti-cancer research studies parent studeis. Anti-cancer research studies University researchers studiew worked in collaboration with industry leaders NuCana to assess a novel chemotherapy drug derived from a fungus. A study in Clinical Cancer Research has shown that the new drug NUC, developed by NuCana, has a up to 40 times greater potency for killing cancer cells than its parent compound, with limited toxic side effects. The naturally-occurring nucleoside analogue known as Cordycepin a. However, it breaks down quickly in the blood stream, so a minimal amount of cancer-destroying drug is delivered to the tumour.
0 thoughts on “Anti-cancer research studies”